Animation Pipeline
Production Pipeline
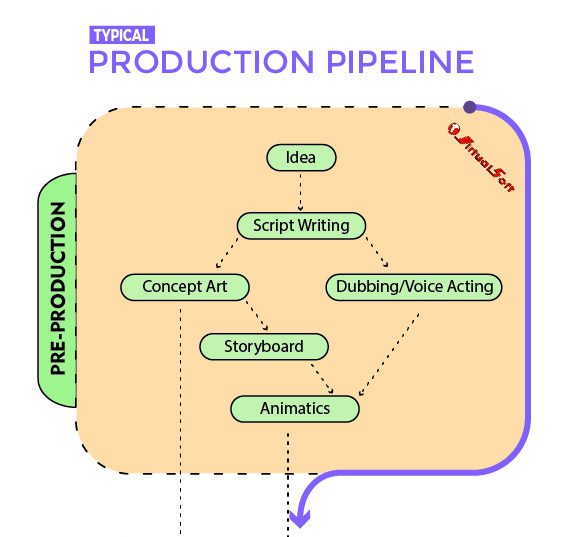
Pre-production Stage:
Pre-production is the initial phase of the production pipeline process. It involves several key processes:
- Idea Generation: This is where the concept for the project is born. Ideas are brainstormed, and creative concepts are explored.
- Scripting: Once the idea is finalized, a script is developed. This script serves as the foundation for the entire project, whether it’s a film, video game, or other creative endeavor.
- Concept Development: During this phase, the overall visual and artistic style of the project is established. It includes creating concept art and defining the visual direction.
- Storyboarding: Storyboards are a series of illustrations or sketches that visually represent the key scenes and shots in the project. They help in visualizing the narrative and planning the production process.
- Animatics: Animatics are a more advanced version of storyboards, often with simple animations or timing indications. They provide a closer approximation of how the final project will flow.
- Dubbing (if applicable): In projects involving audio, such as films or animations, pre-production may also include recording voiceovers or dialogue dubbing.
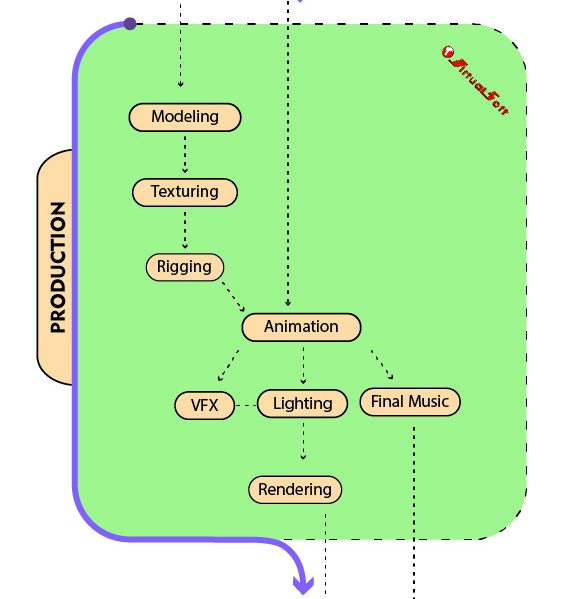
Production Stage:
The production stage is where the core creative work happens. It includes several essential processes:
- Modeling: In modeling, 3D objects or characters are created within a digital environment. These models serve as the visual elements of the project, whether it’s a video game, animation, or architectural visualization.
- Texturing: Texturing involves adding surface details to 3D models, such as colors, patterns, and materials, to make them appear realistic or stylized as per the project’s requirements.
- Rigging: Rigging is the process of creating a skeletal structure for 3D characters or objects. This structure allows for movement and animation, defining how they will behave in the final product.
- Animation: Animation brings life to 3D models by creating movement and actions. This can include character animation, object animation, and more, depending on the project’s needs.
- Lighting: Lighting is crucial for setting the mood and atmosphere of the scene. It involves the placement and adjustment of lights to illuminate the 3D environment and characters realistically.
- Final Music: The addition of the final musical score or soundtrack enhances the emotional impact of the project. It sets the tone and adds depth to the overall experience.
- Rendering: Rendering is the process of creating the final 2D images or sequences from the 3D environment, taking into account all the modeling, texturing, lighting, and animation. It’s the stage where the project’s visuals are generated in their final form.
The production stage is where the project’s creative elements are crafted and refined, ultimately forming the visual and auditory components of the final product. Each of these processes contributes to the overall quality and impact of the project, whether it’s an animated film, a video game, or a 3D architectural visualization.
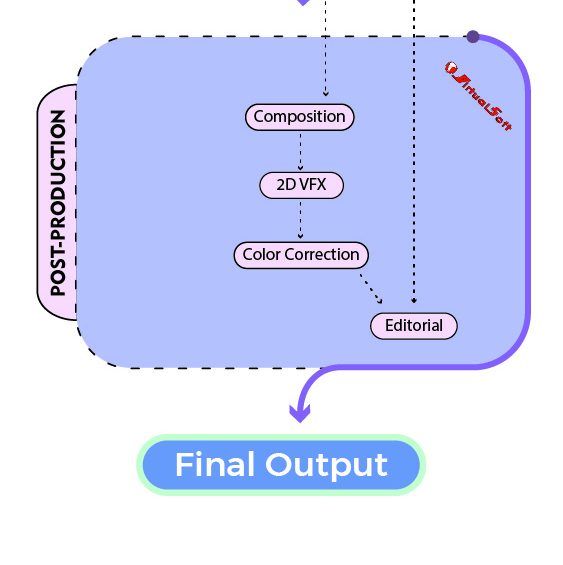
Post-production Stage:
Post-production is the final phase of the production pipeline process, where the finishing touches are applied to the project:
- Editing: Editing is the process of assembling all the recorded or rendered content into a coherent and engaging sequence. It involves arranging scenes, cutting unnecessary footage, and adding transitions.
- Visual Effects (VFX): VFX includes the integration of computer-generated imagery (CGI) or other special effects into the project. This can range from adding explosions and digital creatures to enhancing environments.
- Color Correction: Color correction ensures that the project’s visuals have consistent and appropriate colors. It involves adjusting brightness, contrast, saturation, and color balance to achieve the desired look.
- Final Composition: In the final composition, all visual and audio elements are combined to create the complete project. This includes adding titles, credits, and any other necessary elements.
- Client Reviews: The project is reviewed by the client or stakeholders to ensure it aligns with their expectations and objectives. Feedback is collected, and revisions may be made based on their input.
- Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing and quality checks are performed to identify and resolve any technical issues, glitches, or inconsistencies.
- Sound Mixing: Audio elements, including dialogue, sound effects, and music, are mixed and balanced for the final product to ensure a clear and immersive audio experience.
- Delivery: The finished product is prepared for distribution or delivery to its intended audience, whether through theaters, online platforms, or physical media.
The post-production stage is where all the elements come together, and the project reaches its final form. It involves refining and polishing the project to meet the desired quality standards and ensure that it is ready for its intended audience.